Show Caves as Important Hibernacula of Bats in the Czech Republic

The International Union of Speleology (UIS) has declared 2021 as the International Year of Caves and Karst (IYCK). Unique phenomena in our landscape have therewith received deserved attention. Of more than 2,460 karst caves in the Czech Republic, 14 are show caves. All of them are fully legally protected according to national law and in addition, most of them are also protected as important bat hibernation sites (hibernacula) at the European level pursuant to the European Union’s legislation, namely the Habitats Directive. An important pillar of nature conservation is regular monitoring of Specially Protected animal species, and this also is the case in caves.
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — Research, Surveys and Data Management — Print article in pdf
Monitoring Non-native and Invasive Alien Species in the Czech Republic

Invasive alien species (IAS), together with natural ecosystem fragmentation, degradation, destruction and loss, growing natural-resource consumption, environmental pollution and climate change, are among the main negative factors threatening native species and the biodiversity of native ecosystems. In addition, they can cause high economic damage/financial costs or adversely affect human health. Due to the ability of IAS to spread, an isolated approach to their management at the level of individual regions or countries is usually not effective; we need a targeted and tailored strategy that transcends national borders. Therefore, Regulation (EU) No 1143/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the prevention and management of the introduction and spread of invasive alien species was adopted in the European Union, which was transposed into the Czech Republic’s legal order by amending Act No. 114/1992 Gazette on Nature Conservation and Landscape Protection, and other laws related to the issue, entering into force January 1, 2022.
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — Research, Surveys and Data Management — Print article in pdf
Temporarily Unmown Grass Strips – A Hope for Productive Meadow Insects?

The agri-environmental-climate measures (AECM) announced by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic are intended to support management methods mitigating the negative effects of intensive farming on the landscape and its inhabitants, including insects. Despite their productive nature, permanent grasslands are an important landscape component hosting a wide range of invertebrates. The right balance of production practices and compensatory measures can make a significant contribution to maintaining the diversity of grassland organisms and the ecosystem services they provide. The Nature Conservation Agency of the Czech Republic (NCA CR) has therefore commissioned a study on the effects of temporarily unmown grass strips on the diversity and abundance of meadow organisms. The aim of the study was to verify whether the retained parts of grass stands have a positive effect on the biota on common managed meadows of various sizes.
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — Research, Surveys and Data Management — Print article in pdf
Shall We Go for Krkonoše/Giant Mts. Black Grouses with a Computer?

Yes, this is possible. Although computer modelling will not save the Black grouse, its outputs can significantly help in planning various practical measures in the field, regulating tourists at high-risk sites, and educating visitors. Habitat modelling, which uses the possibilities of geo-information technologies, remote sensing data, and advanced spatial analysis methods (e.g. Hirzel & le lay 2008, ElitH & leatHwick 2009), is applied significantly in the study of ecological requirements of (not only) animal species. These methods, technologies, and data allow extensive analyses of the relationships between the occurrence of species of interest and relevant environmental factors (e.g. Franklin 2010, Guisan et al. 2017). A common approach is to model the current or potential occurrence of species (e.g. tHuiller et al. 2004, Hirzel et al. 2006, Basille et al. 2008); the aim is to determine the landscape potential for their perma- nent or temporary occurrence and to evaluate the significance of individual environmental factors for their spatial expansion. Thus, habitat modelling is currently one of the most widely used approaches in conservation biology (e.g. Huck et al. 2010, Basille et al. 2013, Guisan et al. 2013).
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — Research, Surveys and Data Management — Print article in pdf
Management Agreements: An Important Tool for Cooperation with Landowners and Land Managers in Nature

Ten years ago, the Nature Conservation Agency of the Czech Republic (NCA CR) began to conclude agreements on management through public contracts, setting up both management measures to be implemented and providing landowners or tenants with a subsidy / subvention. Consequently this practice has been step-by-step applied also by other State Nature Conservancy authorities, particularly Regional Offices. At present the agreements on management are one of the principal and commonly used tools in cooperation with land managers. The NCA CR is currently taking active steps to further expand the type of cooperation with landowners, our most important partners in practical nature conservation.
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — Nature and Landscape Management — Print article in pdf
Experience in Training Shepherd Dogs Guarding Livestock

Shepherd dogs guarding livestock are rightly recommended as the most effective measure against grey wolves (Canis lupus) attacking livestock. Farmers are often criticized for hesitating to acquire shepherd dogs. However, few people can imagine the long and challenging journey to a reliable working shepherd dog.
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — Nature and Landscape Management — Print article in pdf
Grassing of Zone I in the Moravian Karst Protected Landscape Area

The Moravský kras/Moravian Karst (central Moravia) is the most important karst area in the Czech Republic. In addition to underground karst phenomena, we can also find surface aboveground karst phenomena there, which include sinkholes and limestone pavements. All these karst phenomena are legally protected. The uniqueness of the area is also confirmed by the only internationally protected underground wetland in the Czech Republic, which is the Podzemní Punkva/Punkva Subterranean Stream Wetland of International Importance (Ramsar Site). The karst environment needs our protection, not only below the surface but also at ground level, from where nitrates and pesticides from intensively managed karst plateaus enter the underground areas. These substances pollute groundwater, which is used as a source of drinking water and harbours a lot of animals. Changes in management around the sinkholes and above the caves implemented in 2019 and 2020, resulted not only in positive shifts in the agricultural landscape, but they also significantly contributed to improving the quality of drip water that seeps down to the caves through the soil and rocks.
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — Nature and Landscape Management — Print article in pdf
Ecosystem Restoration of Brown Coal Open-pit Mines

Mineral and rock mining carried out for centuries has had significantly negative impacts on the landscape and the environment in the Czech Republic. By size, the most extensive destruction in the whole country has been caused by surface open-pit brown coal mining in the Krušné hory/Ore Mountains Foothills Basin, also known as the North Bohemian Basin. More than 400 km2 have been affected by mining and by related infrastructure and industry there. Nowadays, when a termination of active brown coal mining termination in the Sokolov and Most Basins1 has been in sight, the future use of the closed quarries is being discussed extensively. Experts have long been aware of the great scientific significance of abandoned non-reclaimed excavations and spoil heaps. Therefore the question of applying ecosystem restoration to the above post-industrial habitats has been even more urgent than ever before.
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — Nature and Landscape Management — Print article in pdf
Standardization in Nature Conservation and Landscape Management

The Nature Conservation Agency of the Czech Republic (NCA CR) has been for ten years elaborating together with academic institutions standards in nature conservation and landscape protection. Almost thirty such standards have been published yet and approx. the same number has been under preparation. Up-to-date experience shows that the concept of standardization in various activities has proved itself successful and has fulfilled its purpose: standards are used by designers, customers, planners, project implementers, contractors, evaluators of application for a subsidy/subvention/grant and they are also applied in the State/Public Administration performance. Moreover, they are sometimes misapplied. Thus, the standards at present have been serving as a basis for establishing unified code lists of activities in nature conservation and landscape protection linked to costs of common measures and consequently for planning and documenting the interventions having been made in nature and the landscape.
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — Nature and Landscape Management — Print article in pdf
Soil as a Biodiversity Hotspot, Namely that of Small Soil Arthropods
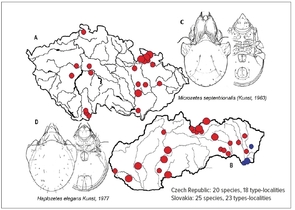
When presenting examples of particularly species-rich ecosystems, we will most probably name tropical coral reefs, tropical gallery forests or selected types of tropical rainforests. To visit these ecosystems, one must travel a long journey far outside of homeland, and even beyond borders of our continent. Still, a comparably species-rich ecosystem can be found, even in our conditions – yet escaping broader awareness when speaking about biodiversity. This is perhaps caused by simple fact, that thousands of species inhabiting this ecosystem could only rarely be observed by the naked eye, as they are mostly of the microscopic size. Indeed, healthy, and well-functioning soil – in our conditions mostly soil of broad-leaved deciduous or mixed forests – is a real biodiversity hotspot reachable just “beyond our courtyards” or next door. Presence of the particular species, overall species richness and relative numbers of soil organisms serves at the same time as great indicator of soil conditions, and often also of the quality of respective above-ground ecosystem at the place.
Nature Conservation 2022 — 25. 5. 2022 — On Nature in the Czech Republic — Print article in pdf

